Body Scientific Aesthetics
7 Key Questions to Help You Decide if Botox Is Right for You
Botox is a prescription neuromodulator (botulinum toxin type A) used to reduce dynamic wrinkles by temporarily relaxing targeted facial muscles. This guide helps you answer seven practical questions—covering eligibility, benefits and risks, cost and durability, and how to choose a qualified provider—so you can decide whether Botox fits your aesthetic goals. Many readers ask, "Is Botox right for me?" or "How can I determine if Botox is the right choice for me?" This article maps clinical considerations, realistic expectations, and follow-up planning into an easy decision flow.
You will learn candidate criteria, common side effects, and aftercare, comparative context versus dermal fillers, ballpark cost and maintenance timing, and a concise checklist of what to ask at consultation. The sections that follow break these topics into actionable steps, short lists for quick decisions, and EAV-style comparison tables to clarify cost, duration, benefits, and provider qualifications. Read through each question to build a coherent plan from self-assessment to a safe, evidence-aware consultation.
Your Decision Framework: 7 Key Questions
To help you navigate the decision-making process, here are the seven essential questions this guide will help you answer:
- Am I a Good Candidate for Botox? Understand the eligibility criteria, including age, medical history, and aesthetic goals.
- What Medical Conditions or History Affect Botox Eligibility? Learn about contraindications and essential disclosures for safety.
- How Do My Aesthetic Goals Align with Botox Treatment? Determine if Botox is the right solution for your specific wrinkle concerns.
- What Are the Benefits and Risks of Botox? Get a clear overview of expected outcomes and potential side effects.
- What Are the Common Side Effects and How Can They Be Managed? Prepare for post-treatment care and recognize red-flag symptoms.
- How Much Does Botox Cost and How Long Do Results Last? Plan your budget and understand the typical duration of effects and maintenance schedule.
- How Do I Choose the Right Botox Provider? Identify key qualifications, experience, and what to expect during consultation.
Am I a Good Candidate for Botox? Key Eligibility Questions
Botox candidacy depends on age, medical history, current medications, and realistic aesthetic goals; it works best for people with dynamic wrinkles caused by muscle movement. Recent research and clinical practice emphasize full medical disclosure—pregnancy, breastfeeding, neuromuscular disorders, or known allergy to botulinum toxin are typical contraindications that require deferral or physician oversight. A systematic self-assessment can help you organize what to disclose and evaluate goals; this approach directs specific eligibility checks to the right clinical questions. Before any treatment, arrange a consultation to verify candidacy and consider alternatives if your goals or medical profile suggest fillers, resurfacing, or energy-based options instead of neuromodulation.
What Medical Conditions or History Affect Botox Eligibility?
Certain health conditions and medications change Botox risk and dosing decisions, so disclosing them is essential for safety. Major contraindications include pregnancy and breastfeeding, active infection at injection sites, and neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; some antibiotics and blood-thinning agents can alter the risk of complications or bruising. Providers typically ask about recent procedures, allergies, and any prior adverse reactions to injectables to tailor a safe plan. If you take medications that affect neuromuscular transmission or clotting, the clinician will review risk mitigation and possibly coordinate care with your physician.
How Do My Aesthetic Goals Align with Botox Treatment?
Botox excels at reducing dynamic lines—those that form with facial expressions—rather than restoring lost volume or changing skin texture. If your primary concern is crow’s feet, forehead creases, or glabellar frown lines, Botox can soften movement-related lines and create a smoother resting appearance; static deep folds or volume loss often need dermal fillers. Combining neuromodulators with fillers or resurfacing can address complex concerns, but clear goal alignment during consultation avoids mismatched expectations. Identifying whether you want prevention (subtle modulation), correction (smoothing pronounced lines), or combination care guides treatment choice and planning.
- Key candidate criteria include age, medical contraindications, current medications, and realistic expectations.
- Candidates for preventative Botox often start earlier to slow dynamic line formation.
- If volume loss or static wrinkles dominate, consider fillers or combined approaches.
These criteria create a practical checklist to bring to your consultation and prepare targeted questions for your practitioner.
What Are the Benefits and Risks of Botox? Understanding Treatment Considerations
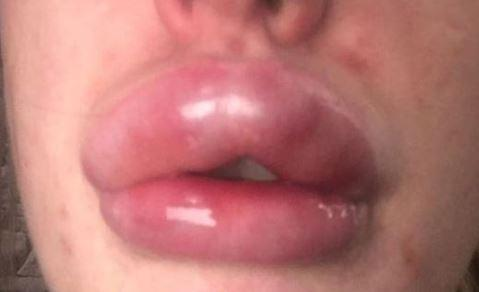
Botox reduces muscle activity by blocking neuromuscular signaling, which softens expression lines and can improve perceived facial balance and symmetry. The primary benefits include temporary wrinkle smoothing, potential preventative effects when used early, and low downtime compared with surgical options; common risks are transient bruising, swelling, mild headache, and rare functional complications like eyelid ptosis. Below is a concise comparison of representative benefits and risks to clarify the mechanism and expected outcomes before you decide.
| Outcome | Mechanism | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|
| Wrinkle smoothing | Neuromuscular blockade reduces muscle contraction | Softer dynamic lines within 3–7 days |
| Preventative modulation | Lower muscle force reduces line deepening over time | Slower progression of expression lines |
| Low-downtime aesthetic change | Local injections with brief recovery | Minimal interruption to daily activities |
The table shows how Botox’s mechanism translates into predictable, temporary outcomes and why management of side effects is part of standard care. Discussing realistic outcomes and contingency plans with a clinician reduces anxiety and supports informed consent.
What Are the Common Side Effects and How Can They Be Managed?
Common post-injection effects are mild and self-limited: localized bruising, tenderness, and transient headache occur most often and usually resolve within days. Management strategies include cold compresses immediately after treatment, avoiding NSAIDs when advised to reduce bleeding risk, and gentle follow-up care instructions from the provider; massage or vigorous rubbing of treated areas is typically discouraged for 24 hours. Recognize red-flag symptoms—sudden vision changes, difficulty breathing, or generalized muscle weakness—and seek urgent medical attention if they arise. Most clinics provide explicit post-care guidance and a protocol for reporting and managing unexpected reactions.
How Does Botox Improve Wrinkles and Facial Appearance?
Botox targets dynamic wrinkles by interrupting the signal at the neuromuscular junction, preventing repetitive micro-contractions that create creases over time. Onset of visible effect commonly begins within 3–7 days, with peak smoothing at about two weeks, and gradual return of movement over three to six months, depending on dose and muscle strength. For deeper static lines, combining Botox with fillers yields more comprehensive improvement: neuromodulation relaxes muscles while fillers restore volume in adjacent areas. Expect modest, natural-looking changes when dosing is conservative and aligned with your facial anatomy and aesthetic goals.
How Much Does Botox Cost and How Long Do Results Last?
Average cost and duration vary by treatment area, units used, and practitioner pricing model; typical effects last about 3–6 months, and maintenance scheduling depends on individual metabolism and muscle activity. Pricing models include per-unit billing and per-area or per-treatment pricing; choosing a provider based solely on the lowest cost can increase the risk of poor technique or over/under treatment.
The table below compares common treatment areas by average units, cost factors, and expected maintenance intervals to help you budget and plan follow-up.
| Treatment Area | Typical Units (approx.) | Typical Duration / Re-treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Glabella (frown lines) | Moderate units | 3–4 months on average |
| Forehead lines | Variable units | 3–5 months, depending on strength |
| Crow’s feet | Lower to moderate units | 3–6 months, often longer with lower doses |
This comparison clarifies that duration is predictable but individualized; planning treatments on a 3–6 month cadence helps maintain results and lets you adjust dosing over time.
What Is the Average Cost of Botox Treatments?
Pricing is commonly presented as per-unit or per-area; per-unit billing ties cost to the number of botulinum toxin units used, while per-area pricing groups multiple units into a single fee for a region such as the forehead or glabella. Typical ballpark ranges depend on local market and provider expertise, and overly low prices can indicate inexperienced injectors or diluted products—prioritize qualifications over the lowest cost. During consultation, ask whether pricing reflects genuine unit counts, what the expected number of units for your goals will be, and whether follow-up touch-ups are included.
How Often Will I Need Botox to Maintain Results?
Most patients schedule retreatment every 3–6 months, with variability driven by metabolic rate, muscle strength, and treatment dose; some areas and individuals sustain results longer. Tracking how long you personally maintain the effect after an initial series helps refine interval timing and can reduce total units over time if muscles weaken gradually. Providers may recommend an initial follow-up around two weeks to assess response and a maintenance plan based on your goals—preventative spacing differs from correction-focused scheduling. A consistent maintenance strategy supports both aesthetic continuity and safer dose adjustments.
How Do I Choose the Right Botox Provider? Essential Questions to Ask
Choosing a provider hinges on verified medical credentials, documented injectables training, and a transparent consultation process that prioritizes safety and realistic outcomes. Treat provider selection as a systematic process where you map credentials, experience, informed consent practices, and complication protocols to specific decision points during your consultation. Look for clear before/after documentation, willingness to review your full medical history, and a consultation that explains risks, alternatives, and expected timelines. Asking targeted questions and comparing responses across practitioners reduces risk and improves the chance of a satisfactory aesthetic outcome.
| Practitioner Type | Key Qualification | What That Means for Safety/Results |
|---|---|---|
| Board-certified dermatologist | Specialty training in skin and injectables | Deep anatomical knowledge; strong safety focus |
| Plastic surgeon | Surgical and facial anatomy expertise | Useful for complex structural changes and managing complications |
| Nurse practitioner / PA with specialized injectable training | Advanced practice clinicians with training certificates | Can deliver competent results when supervised and properly credentialed |
What Qualifications and Experience Should a Botox Practitioner Have?
Important credentials include medical licensure, documented injectable-specific training, and clear evidence of ongoing education in aesthetic techniques; board certification in dermatology or plastic surgery is an added marker but not the sole determinant of competence. Experience indicators include years performing injections, a robust before-and-after portfolio, and transparent complication protocols; ask about the volume of similar treatments performed and examples of outcomes for your target areas. Verification can include requesting training certificates and reading patient education materials they provide. A skilled injector explains anatomy, tailors the dose to muscle strength, and outlines contingency plans for rare adverse events.
What Should I Expect During the Consultation and Treatment Process?
A thorough consultation reviews medical history, contraindications, photos or markings of target areas, consent discussion, and a tailored treatment plan with dose rationale and aftercare instructions. During the injection visit, expect site marking, measured dosing, brief injections with minimal downtime, and immediate post-procedure guidance, including cold therapy and activity precautions. Ask about follow-up timing (commonly two weeks) for result assessment and any touch-ups, plus clear instructions on when to seek urgent care for unexpected symptoms. This transparent workflow supports safety, aligns expectations, and provides a roadmap for maintenance and future adjustments.
A final decision framework brings together eligibility, realistic benefits and risks, cost planning, and provider selection into a practical action plan. Use the lists, tables, and checklist above to prepare focused questions and share your goals and medical history openly at the consultation to ensure a safe, evidence-informed outcome.